What is an RF Leaky Feeder Cable and How is it Constructed?

RF leaky feeder cables, also known as radiating cables, play a critical role in extending wireless communication in environments where traditional antennas fail to provide reliable coverage. These cables are designed to emit and receive radio frequency (RF) signals along their length, making them indispensable in underground mines, tunnels, trains, and large buildings.
In this blog, we’ll explain what a leaky feeder cable is, how it works, and how it’s constructed to provide seamless RF coverage.
What is an RF Leaky Feeder Cable?
A leaky feeder cable is a specialized type of coaxial cable that acts as both a signal transmission line and an antenna. Unlike standard coaxial cables, which are designed to contain RF signals within the cable, leaky feeders are intentionally designed to "leak" signals at controlled intervals along their length.
Key Features:
- Bidirectional Communication: Leaky feeder cables can transmit and receive signals, enabling two-way communication for radios, cellular devices, or other RF systems.
- Signal Propagation Along the Cable: Signals are radiated uniformly along the cable, providing consistent coverage in areas where signal penetration is otherwise limited.
- Customizable Signal Loss: The amount of signal leakage can be tailored during construction to meet specific coverage needs.
How Does a Leaky Feeder Cable Work?
Leaky feeder cables function as distributed antennas. When connected to a base station, the cable carries RF signals and emits them along its length through controlled slots, openings, perforations, or apertures in the cable’s shielding. The illustration below shows a comparison of typical RF cable construction vs. a leaky feeder specific RF cable design.
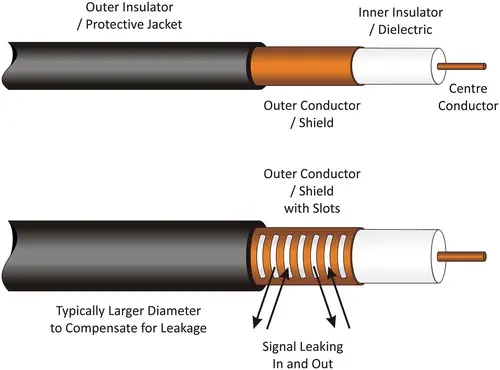
These openings allow RF signals to escape and provide coverage, while also enabling the cable to pick up incoming signals from nearby devices. By coupling the cable with amplifiers or repeaters, the signal strength can be maintained over long distances.
Construction of a Leaky Feeder Cable
The unique performance of a leaky feeder cable is a result of its specialized construction. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
1. Center Conductor
- Material: Typically made of copper or copper-clad aluminum for high conductivity.
- Function: Transmits the RF signal along the cable.
2. Dielectric Layer
- Material: Polyethylene (PE), foam PE, or PTFE.
- Function: Insulates the center conductor and maintains the cable’s impedance. The dielectric layer helps to minimize signal loss and ensures uniform propagation of RF signals.
3. Shielding with Controlled Openings
- Material: Metallic foil or braided copper shielding.
- Design: The shielding is designed with intentional gaps, perforations, or slots to allow RF energy to radiate outward. These openings are precisely engineered to control the amount of signal leakage along the cable’s length.
- Function: Balances the containment and radiation of signals, ensuring the cable performs as both a transmission line and an antenna.
4. Outer Jacket
- Material: Durable polyethylene, polyurethane, or PVC.
- Function: Protects the cable from physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and environmental wear. In harsh environments like mines or tunnels, the jacket may include flame-retardant or low-smoke materials.
5. Additional Features
- Armoring: Some leaky feeder cables are armored with additional layers of steel or ruggedized materials for added protection in industrial or underground environments.
- Waterproofing: Many leaky feeder cables are constructed with water-resistant coatings or sealed jackets to prevent moisture ingress.
Applications of RF Leaky Feeder Cables
Leaky feeder cables are used in environments where traditional wireless networks struggle to provide reliable signal coverage. Common applications include:
- Underground Mines:
- Provides communication between workers and control centers.
- Enables real-time tracking and monitoring of equipment.
- Tunnels:
- Facilitates cellular and radio communication in road and rail tunnels.
- Enhances safety by ensuring emergency communication systems are always operational.
- Buildings:
- Extends wireless coverage in large, dense buildings like hospitals, shopping malls, and airports.
- Trains and Subways:
- Enables uninterrupted communication for passengers and operators within train cars and tunnels.
Advantages of Leaky Feeder Cables
- Continuous Coverage: Eliminates dead zones in challenging environments.
- Customizable Signal Radiation: Signal strength and leakage patterns can be tailored to specific needs.
- Durability: Rugged construction ensures reliable performance in harsh or demanding conditions.
- Scalability: Easily integrated with amplifiers and repeaters to extend coverage over long distances.
Conclusion
RF leaky feeder cables are an elegant solution for extending wireless communication in environments where traditional antennas fail. Their unique construction, featuring controlled shielding perforations, allows them to act as both transmission lines and distributed antennas.
By understanding how leaky feeder cables are constructed and how they work, engineers can design effective communication systems for challenging environments like tunnels, underground mines, and dense buildings. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable for maintaining seamless connectivity where it’s needed most.

About Dean Gammell
Dean Gammell leads customer facing efforts for ConductRF and manage the product support strategy focused on key customers and markets with a heavy emphasis on application engineered solutions.



